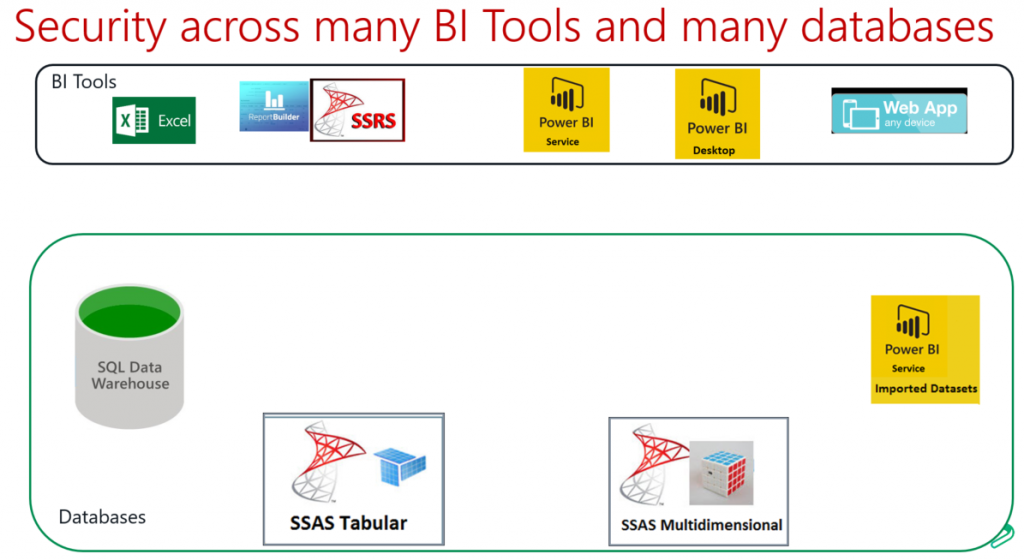
In this article, I’ll show the implementation of Row-Level-Security (RLS) with SQL 2016 and any .NET application like Web MVC, Web Forms, Web API, Windows App, etc. In previous articles, I showed you how to implement RLS in SQL 2016 and how client tools like Excel or Power BI can take advantage of this security. Now we’ll focus in .NET applications. Traditionally, we use to implement the security for data by coding the necessary logic using C# or VB.NET in the middle tier application.
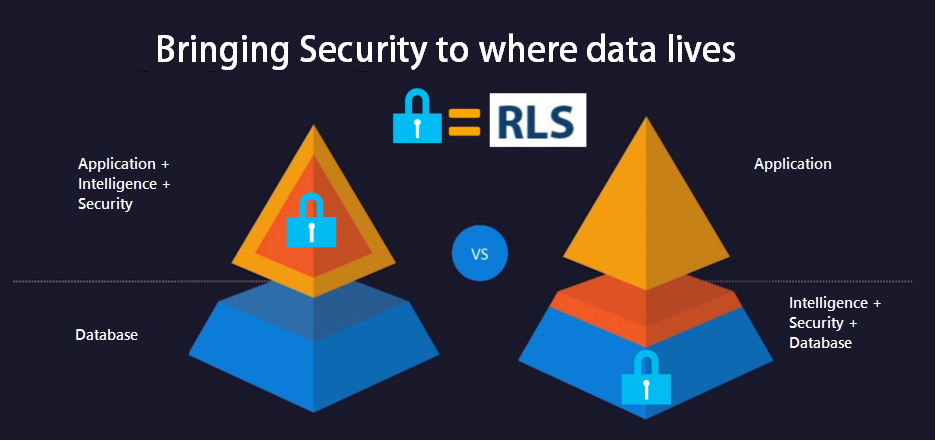
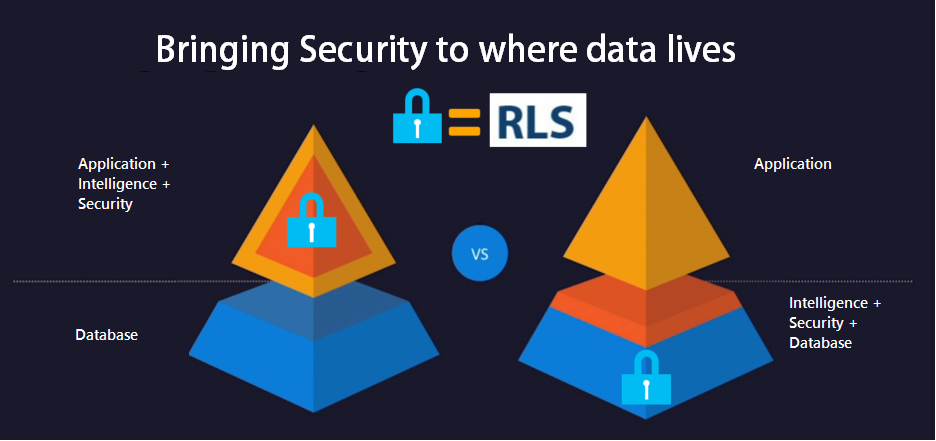
Now, SQL 2016 allows the implementation of RLS, the security logic can be implemented right in the database, reducing the security code in the .NET middle tier app and centralizing the security in the source database, so any application or third party tool can connect to the database and reuse the same RLS security.
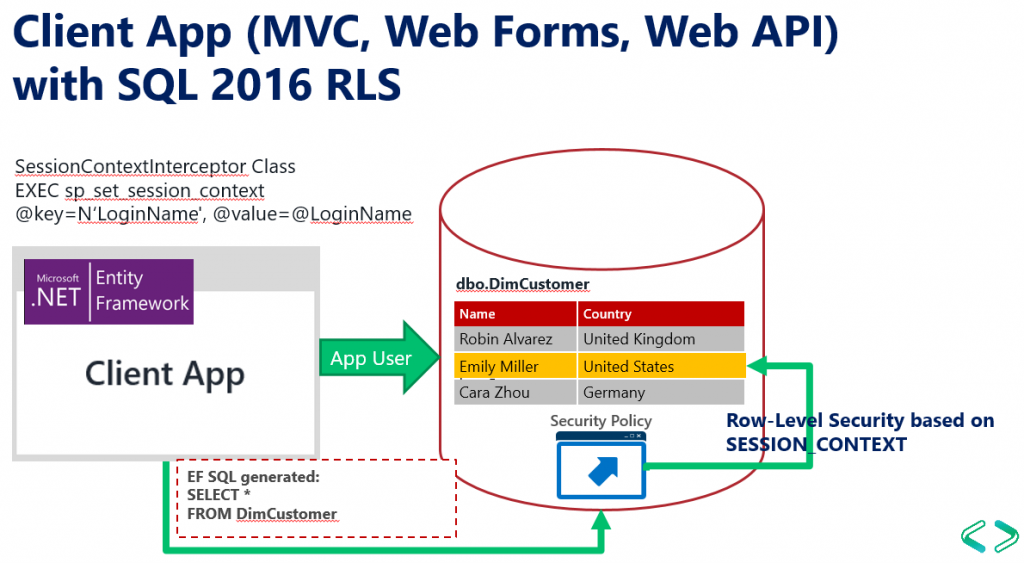
The following sample shows how to implement RLS in SQL to allow any .NET application with or without Active Directory or using another Security Membership Framework to query a SQL Server 2016 database and use RLS.
In order to do this, the .NET application should set values in the SESSION_CONTEXT after connecting to the database, and then security policies in the database will be able to read the values from SESSION_CONTEXT and filter rows using the Context values.
This article uses the same database I use in other articles.
In Visual Studio, Create Wasp – ASP .NET Project – Check ASP Forms and MVC. You can implement this in any .NET Windows or Web application: Console App, MVC, Web API, etc. For simplicity we’ll use Web Forms, but you might also implement this using Web API and use Angular for your web app.
Select MVC Template, Windows Authentication.
Add new item to the project: ADO.NET Entity Data Model, to the sample database. This will create a reference to Entity Framework. Call the model AdventureWorksModel.
Build the connection to the database.

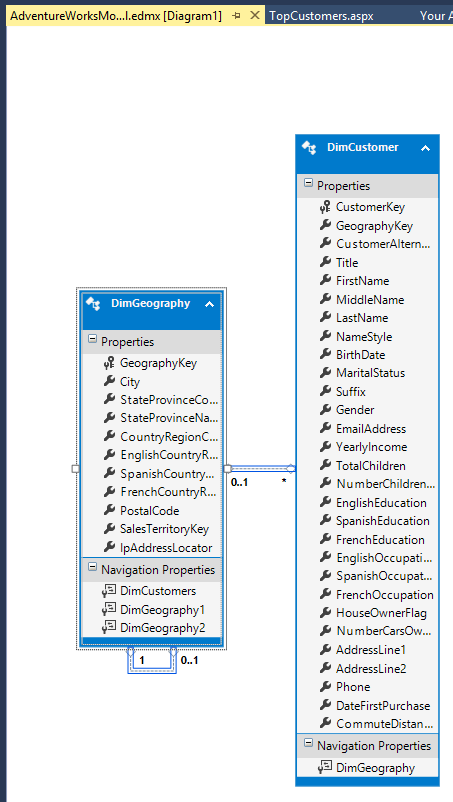
For this sample, we’ll chose the tables DimCustomer and DimGeography.

You’ll get this model.
Create a Web Form called: TopCustomers.aspx. Add a RadGrid and ScriptManager Control to the Form. Add this code to code behind file TopCustomers.aspx.cs:
I add a Telerik Radgrid (You can add any control you want to display a list of customers) and the script manager.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
namespace WebAppWithRLS
{
public partial class TopCustomers : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
AdventureWorksDW2014Entities db = new AdventureWorksDW2014Entities();
var topCustomers =
from customer in db.DimCustomers
join geography in db.DimGeographies on customer.GeographyKey equals geography.GeographyKey
select new { Name = customer.FirstName + " " + customer.LastName, geography.EnglishCountryRegionName };
RadGrid1.DataSource = topCustomers.ToList().Take(100);
RadGrid1.DataBind();
}
}
Set the TopCustomers.aspx page as “Start Page”

Run the application in Visual Studio.

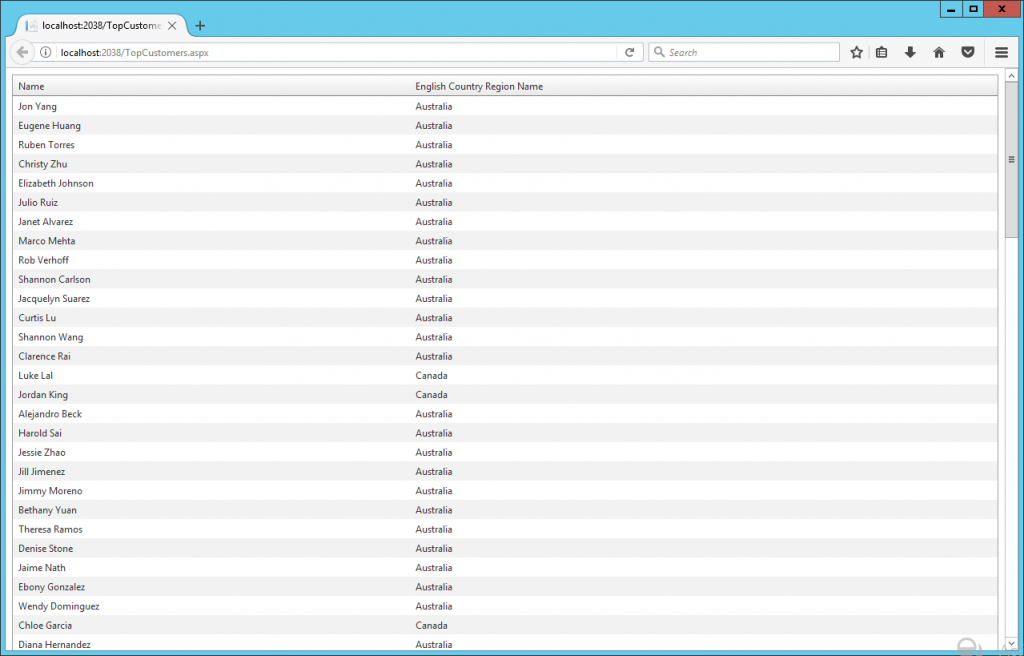
The page shows records from Australia and Canada. Even though the user gwilliams belongs to the Active Directory group “AW United Kingdom” so it should retrieve customer records from England only.
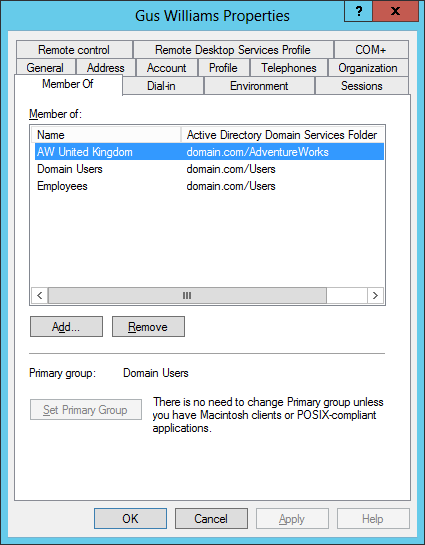
The user gwilliams is logged to the ASP .NET application, even though the Web App becomes a middle tier application that connects to the database using another middle tier user. In visual studio is the user account executing running visual studio and in IIS is the AppPool configured user.
The way to resolve go around this scenario is to send the context values in our context session before executing the SQL query or command, so SQL 2016 RLS can read this values and apply the corresponding security.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Data.Common;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.Interception;
namespace WebAppWithRLS.Models
{
public class SessionContextInterceptor: IDbConnectionInterceptor
{
public void Opened(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext interceptionContext)
{
// Set SESSION_CONTEXT to current UserId whenever EF opens a connection
try
{
var loginName = System.Web.HttpContext.Current.User.Identity.Name;
if (loginName != null)
{
DbCommand cmd = connection.CreateCommand();
cmd.CommandText = "EXEC sp_set_session_context @key=N'LoginName', @value=@LoginName";
DbParameter param = cmd.CreateParameter();
param.ParameterName = "@LoginName";
param.Value = loginName;
cmd.Parameters.Add(param);
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
} catch (System.NullReferenceException)
{
// If no user is logged in, leave SESSION_CONTEXT null (all rows will be filtered)
}
}
public void Opening(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext interceptionContext)
{
}
public void BeganTransaction(DbConnection connection, BeginTransactionInterceptionContext interceptionContext)
{
}
public void BeginningTransaction(DbConnection connection, BeginTransactionInterceptionContext interceptionContext)
{
}
public void Closed(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext interceptionContext)
{
}
public void Closing(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext interceptionContext)
{
}
public void ConnectionStringGetting(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext < string > interceptionContext)
{
}
public void ConnectionStringGot(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext < string > interceptionContext)
{
}
public void ConnectionStringSet(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionPropertyInterceptionContext < string > interceptionContext)
{
}
public void ConnectionStringSetting(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionPropertyInterceptionContext < string > interceptionContext)
{
}
public void ConnectionTimeoutGetting(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext < int > interceptionContext)
{
}
public void ConnectionTimeoutGot(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext < int > interceptionContext)
{
}
public void DataSourceGetting(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext < string > interceptionContext)
{
}
public void DataSourceGot(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext < string > interceptionContext)
{
}
public void DatabaseGetting(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext < string > interceptionContext)
{
}
public void DatabaseGot(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext < string > interceptionContext)
{
}
public void Disposed(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext interceptionContext)
{
}
public void Disposing(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext interceptionContext)
{
}
public void EnlistedTransaction(DbConnection connection, EnlistTransactionInterceptionContext interceptionContext)
{
}
public void EnlistingTransaction(DbConnection connection, EnlistTransactionInterceptionContext interceptionContext)
{
}
public void ServerVersionGetting(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext < string > interceptionContext)
{
}
public void ServerVersionGot(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext < string > interceptionContext)
{
}
public void StateGetting(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext < System.Data.ConnectionState > interceptionContext)
{
}
public void StateGot(DbConnection connection, DbConnectionInterceptionContext < System.Data.ConnectionState > interceptionContext)
{
}
}
public class SessionContextConfiguration: DbConfiguration
{
public SessionContextConfiguration()
{
AddInterceptor(new SessionContextInterceptor());
}
}
}
Create the class SessionContextInterceptor.cs and add the following code:
The class SessionContextInterceptor as the name suggest will intercept a SQL command from EF model and execute the code in the Opened method. Using sp_set_session_context we set the value of @LoginName variable. This variable will be alive and accessible form SQL Server only for that session.
Now, let’s implement the RLS in SQL. We create the predicate function which reads the context values using SESSION_CONTEXT(N’LoginName’).
USE [AdventureWorksDW2014]
GO
CREATE FUNCTION RLS.GeographyAccessPredicate(@GeographyKey AS INT)
RETURNS TABLE
WITH SCHEMABINDING
AS
RETURN SELECT 1 AS AccessResult
FROM dbo.DimGeography G
INNER JOIN dbo.DimActiveDirectoryUser U
ON G.GeographyKey = @GeographyKey AND
(
(
U.LoginName = CAST(SESSION_CONTEXT(N'LoginName') AS nvarchar(150))
OR
U.LoginName = REPLACE(SUSER_NAME(), 'DOMAIN\', '')
)
AND
G.EnglishCountryRegionName = REPLACE(U.GroupName,'AW ','')
)
GO
CREATE SECURITY POLICY RLS.AWSecurityPolicy
ADD FILTER PREDICATE RLS.GeographyAccessPredicate(GeographyKey) ON dbo.DimCustomer
After that we run he program and now we can see only customers from United Kingdom, so the records are filtered by using the user name gwilliams.
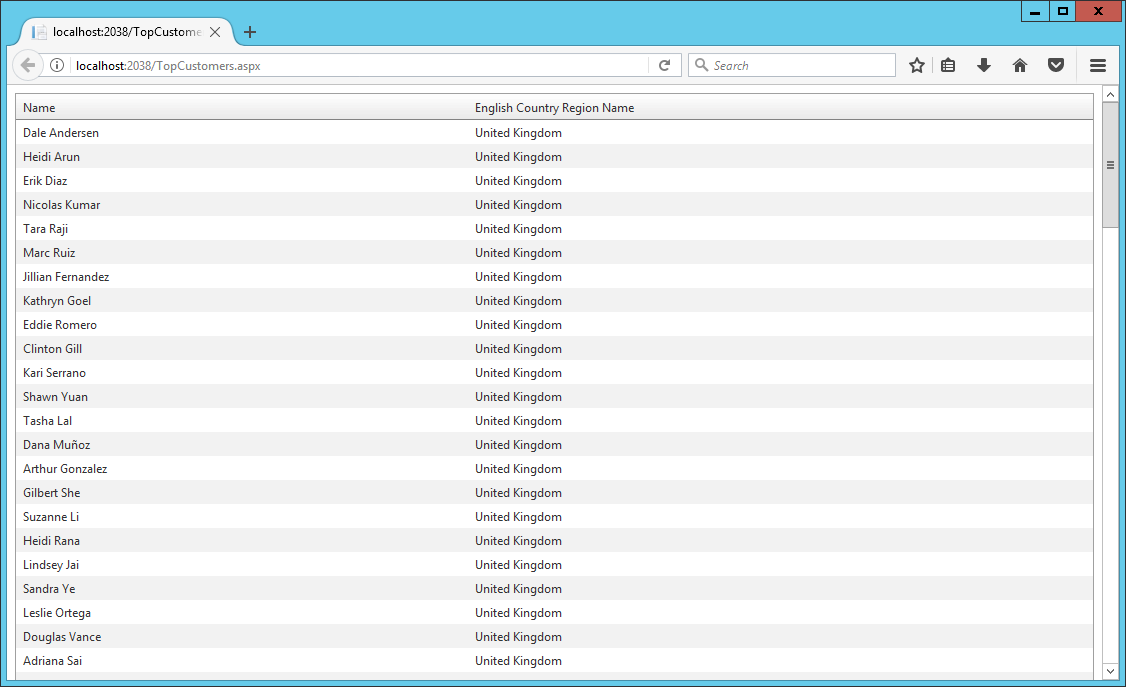
In this article, I showed how RLS can be implemented regardless of the type of authentication (Database Custom Membership, Windows, Forms, OWIN, etc.) in our .NET application and type of .NET application: Console App, Window App, Web API, ASP .NET MVC/Web Forms, etc.