The following is a series of articles that explain how we can use Row Level Security (RLS) and Active Directory across all BI technologies, database and tools in the corporate environment.
The goal is to create an integrated and a comprehensive data access control across multiple database technologies using different BI Tools or Apps.
SQL Server 2016 and Power BI started to support Row-Level-Security last year. RLS was already supported by SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) with Tabular and Multidimensional for some time.
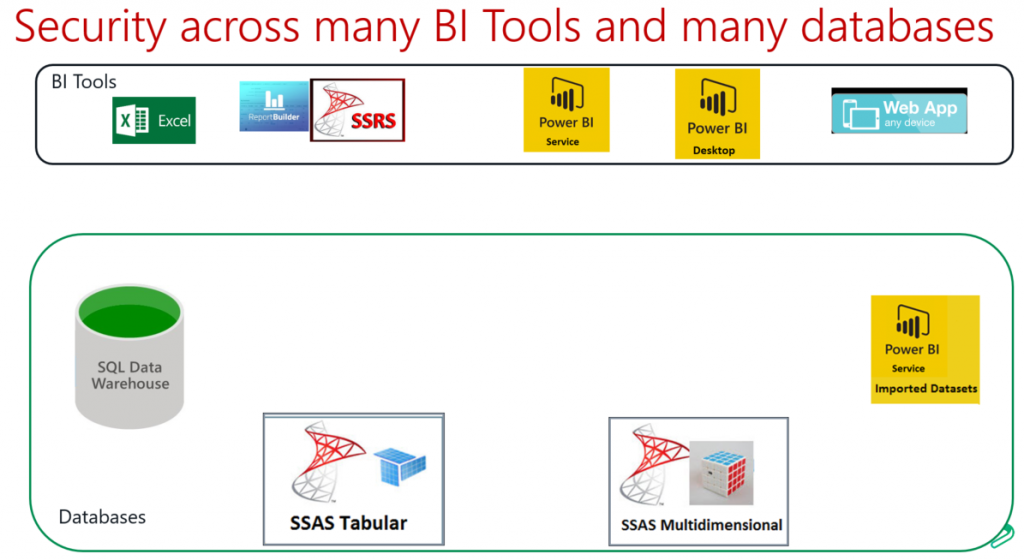
The following picture shows some BI Tools and Databases used in the Microsoft BI Ecosystem.
On the top we have BI Tools used for authoring, publishing and hosting reports like:
- Excel, number one BI Tool in the world, which can get data from a large variety of data sources and use it in Excel with Power Pivot or Power Query.
- Report Builder to author printed paginated reports that can be share and published using the in SSRS Portal.
- Power BI Desktop to author interactive visualizations with analytics capabilities.
- Power BI Service, which is the portal that host Dashboards and Power BI reports.
- We also can have Web Applications using Microsoft .NET MVC or Web Forms with Entity Framework that connect to any of these data sources.
On the bottom we have a variety of databases:
- SQL Server Relational database, which could be an online transactional processing (OLTP) databases or Online analytical processing (OLAP) database, when use it as a data warehouse.
- SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) Tabular Mode
- SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) Multidimensional Mode
- Power BI Imported Datasets, which are very similar to Tabular databases, but hosted on the cloud (Power BI Service) instead of on premise.
Traditionally, BI applications used to implement all rules regarding the data security within the application. For example we can have a BI App that implement security that allow users or group of users to access only to some specific set of data. The problem with this approach is it does not allow to reuse this security among other BI Tools. For example we can have security implemented in SSRS for folders and report level permissions or connections. Even though this SSRS security cannot be reused by Power BI nor Excel.
The best place to implement the security is right within the database, where the security can be centralized and maintained in only one place. On this way, any BI Tool or any App that uses the database, will also use the implemented security without the need to implement security in every single Web App or Tool.
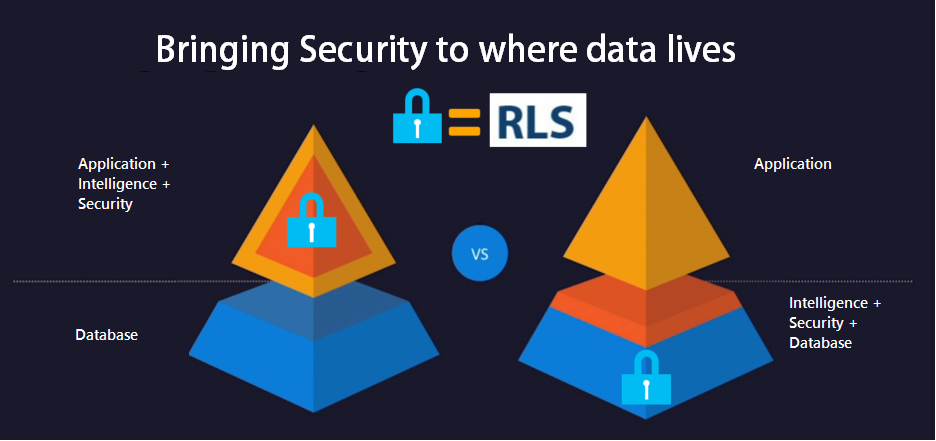
The following picture shows a comparison of a database and application features. Business Intelligence and Security used to be common responsibilities of and application. Now databases have more powerful features in terms of business intelligence and security and these responsibilities can be implemented now in the database.
In order to implement a centralized and reusable security, we have to use these two security features available in all databases (Relational SQL, SSAS Tabular, SSAS Multidimensional):
- Row Level Security (RLS) and
- Active Directory (AD) Groups.
Implementing security in the database using RLS and AD give us the flexibility to use any BI tool that can connect to our database using an Active Directory account and our database will be protected using centralized security rules implemented right in the database.
In the following articles, I will implemented RLS and AD security across all these technologies and all BI tools. In these articles I will be share code samples, I’ll show How to unit test the security and also How to troubleshoot the security.
The following list is the series of articles to be publish related with this topic:
SQL Server 2016 On-Premise with Row-Level Security with Active Directory (Part I)
SQL Server 2016 On-Premise with Row-Level Security with Active Directory (Part II)
SSAS 2016 Tabular On Premise with Row-Level Security and Active Directory.
Client App Security (MVC, Web Forms, Web API) with SQL 2016 RLS and Active Directory
Power BI Security with Active Directory Synch and On-Premise Data Gateway.
Power BI using SSAS Tabular with Row Level Security.
Power BI using SSAS Multidimensional with Row Level Security.
Power BI – Imported Data with Row Level Security.
Power BI – Direct Query with Row Level Security.
Power BI: Integrate Power BI dashboard with a web application.